Over the past 200 years, the world has witnessed some amazing transformations. One industry that has revolutionised the modern world is the automobile sector. It all started in the year 1901 when Mercedes received credit for being the first modern motor car. Before that, the major form of transportation was the horse. Later, Mr. Henry Ford innovated the mass production technique for car manufacturing. Since then, the U.S., Germany, and Japan have been the biggest players in the automobile industry. In just 100 years, the car industry has made leaps and bounds in innovation, but that was not the end.

The 19th-century car used an internal combustion engine (ICE) that required petrol or diesel. However, there was an alternate technology that used electricity powered by a battery. However, for many reasons, electric cars never became mainstream in the 19th century until Tesla introduced its car Roadster in 2008. With that, Tesla began a new revolution in the automobile industry. This could also be called one of the biggest revolutions of the 21st century: the rise of the electric vehicle industry.
The Global Electric Vehicle Market
Hello everyone, my name is Sahil, and this is my Personal Finance Academy, where I explain everything about money management in layman’s language. Recently, many of you have requested a video on the electric vehicle industry and its future in India. So, I did a lot of research and created two videos. This is the first part of the video, where I have explored the global electric vehicle industry, the current state of the electric vehicle market, future growth prospects, and key players in the global electric vehicle industry. Then I have analysed the Indian electric vehicle market, the current state of the electric vehicle market in India, major challenges, key initiatives to overcome the challenges, and the future growth prospects.
Current State of the Electric Vehicle Market
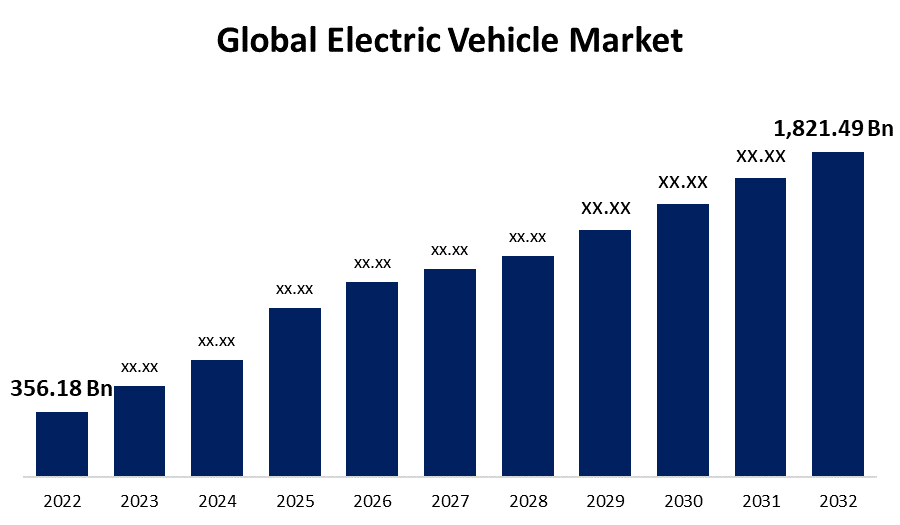
After the U.S., Japan, and Germany dominated the petrol-diesel car market, everyone was in the race to capture the electric vehicle market to rule the 21st-century automobile industry. If you look at the current state of electric car sales globally, the total sales of electric cars in FY19 stood at 2.3 million units. This number was in the few thousand in 2013. So, within seven years, electric vehicle sales have grown multiple times. Despite such huge growth, only 2.5% of the world’s passenger vehicles run on electricity. So, you can imagine the kind of growth prospects.
Globally, there are mainly three markets that represent 94% of total EV sales: the U.S., Europe, and China. If I ask you which is the biggest global market for electric vehicles, you would probably answer the U.S., right? Well, you would be surprised to know that China is the biggest global market for electric vehicles, with around 1.2 million units sold in FY19, which is almost half of total EV sales worldwide. It is followed by Europe with 0.6 million EV sales, and the U.S. is in third position with 0.3 million electric vehicle sales.
Future Growth Prospects
In terms of market share, electric vehicles in China accounted for just five per cent of the total vehicle market in FY19. EVs in Europe have a 3% market share, and the U.S. electric vehicle market contributes 2% to the total market share. In other words, we can say that this is just the beginning of the EV market. As per a report from McKinsey, the electric vehicle market is going to explode in the next 10 years. The electric vehicle market in China is expected to rise from 7 percent in 2020 to 37 to 52 percent by 2030. The European market is expected to increase from 7% in 2020 to 33 to 34% by 2030, and the U.S. market is expected to increase from 3% in 2020 to 17 to 36% by 2030. This means that in the next 10 years, the China market is expected to grow around 5-7 times, the European market is expected to grow around 5 to 6 times, and the U.S. market is expected to grow 6 to 12 times. These are just crazy growth numbers!
Key Growth Drivers in the Global Market
The first driver is government policies. Governments have created policies regarding CO2 emission limits and are encouraging car manufacturers to produce more fuel-efficient vehicles. The second reason is incentivization. Governments are incentivizing electric vehicle purchases with subsidies, tax breaks, and various other monetary incentives. The third reason is charging stations. One of the major reasons for growth in the U.S., Europe, and China is the setup of charging stations by the government as well as private players. By the end of 2019, there were about 7.3 million chargers worldwide, out of which 6.5 million were private.
Key Players in the Global Electric Vehicle Market
The global electric vehicle market is dominated by major players such as Tesla, BYD (a Chinese company), BMW and Volkswagen (German companies), and Nissan (a Japanese company). Tesla captures around 28% of the total electric vehicle market in the first half of 2020. There is high consumer demand for Tesla cars due to their innovative technology, modern design, and high performance.

The Indian Electric Vehicle Market
Electric vehicles represent less than one per cent of the total automobile market in India. Yes, it is a very small market as of now. India is predominantly a two-wheeler market, with more than eighty per cent of internal combustion engine sales coming from two-wheelers. The penetration of electric vehicles in the four-wheeler segment has remained extremely low at 0.1%.
Challenges in the Indian Electric Vehicle Market
The first challenge is high prices. At the end of the day, cost would be a key parameter for electric vehicle adoption in India. To address this challenge, the central government’s Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Hybrid and EV (FAME) policy is offering monetary incentives to customers, which would reduce the purchase price of electric vehicles and bridge the price differential between electric vehicles and internal combustion engine vehicles. Under the FAME 2 policy, the government has announced a total incentive of Rs 10,000 crore between the period FY 20 to 22. Apart from this, there are various other incentives like road tax and registration fee exemptions, etc.

In terms of upfront cost, two-wheelers and three-wheelers are already competitive. However, four-wheeler personal and commercial vehicle costs are almost two to two and a half times higher. If you look at the expected time for total cost of ownership with subsidy, two-wheelers and three-wheelers are already at par with ICE. However, four-wheeler passenger cars would take until 2025 to be at par with internal combustion engine costs of ownership. Without the subsidy, four-wheeler passenger cars would take another 10 years to be at par with internal combustion engine costs of ownership.
Initiatives to Overcome Challenges
The second reason is the lack of options in the EV segment. As of now, there are limited options in the electric vehicle category in India. State governments are incentivising companies to attract investment in the EV sector. The government has also kept the GST on EVs and EV chargers at five percent.
The third reason is the underdeveloped ecosystem of battery production and charging stations. For large-scale electric vehicle adoption, it is very critical to build an ecosystem of battery industries and charging infrastructure. For example, currently, lithium-ion battery cell production hubs are primarily located in China, the U.S., Europe, Japan, and South Korea. The Indian government wants to promote the manufacturing of electric vehicles in India, with plans to build Tesla-style giga factories and develop a homegrown battery manufacturing ecosystem as well as a network of charging stations.
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has transferred its in-house lithium-ion technology at a nominal fee of Rs 1 crore to 10 Indian industries for commercial production. This move is expected to lead to the establishment of lithium-ion cell manufacturing facilities for indigenous electric vehicles. The Indian government has recently sanctioned 2,636 public charging stations in 62 cities. Out of these, 1,633 charging stations are expected to be fast-charging stations and 1,003 slow-charging stations. With this, 20,000 charging points are expected to be installed across selected cities.
Future Growth Prospects in India
Policymakers in India have been actively pushing EV adoption in recent years. The government think tank NITI Aayog has specified that FAME 2 and other policies supporting electric mobility are expected to push EV sales penetration to thirty per cent for private cars, seventy per cent for commercial cars, forty per cent for buses, and eighty per cent for two-wheelers and three-wheelers by 2030. Based on the analysis of key enablers for electric vehicles, KPMG in India expects 25 to 30% two-wheeler penetration and 65 to 75% three-wheel adoption by 2030. However, four-wheeler passenger vehicle electrification is expected to lag, with 10 to 15% penetration in the personal segment and 20 to 30% penetration in the commercial segment by 2030. About 10 to 12% of the overall market for buses is expected to be electrified by 2030. There is a bright future for the growth of electric vehicles in India.
With this, we have come to the end of this discussion. I hope you have a good understanding of the global electric vehicle market and the Indian electric vehicle market, along with the various challenges, opportunities, and future growth prospects. What do you think about the future of electric vehicles? Do let me know your thoughts in the comment box. In the second part, we will discuss the key players in the electric vehicle segment in India. I do a lot of research to create such informative content for you, so do like and share this post and subscribe to this channel, as it would motivate me to come up with more such informative content in the future.
