In the realm of renewable energy, solar panels have become a household name. Most of us are familiar with the traditional silicon solar panels that convert sunlight into electricity, which can then be stored in batteries for later use. However, a new player is emerging in the field: the hydrogen solar panel. This innovative technology offers a range of applications beyond electricity generation, potentially revolutionising the way we harness and utilise solar energy.

Understanding Traditional Solar Panels
Before diving into the specifics of hydrogen solar panels, let’s first understand the basic functionality of traditional silicon solar panels. When installed on rooftops, these panels capture sunlight and convert it into electricity through photovoltaic cells. This electricity can be stored in batteries for use during nighttime or cloudy days. Additionally, users can opt for net metering, a system where excess electricity generated during the day is fed back into the grid, and the user receives credit for it.

The Basics of Hydrogen Solar Panels
The hydrogen solar panel is a step ahead in terms of functionality. Unlike traditional panels, these panels not only generate electricity but also produce hydrogen fuel, a powerful energy source. The hydrogen solar panel appears similar to traditional panels but with distinct differences in its components and design, allowing for dual functionality.
How Hydrogen Solar Panels Work
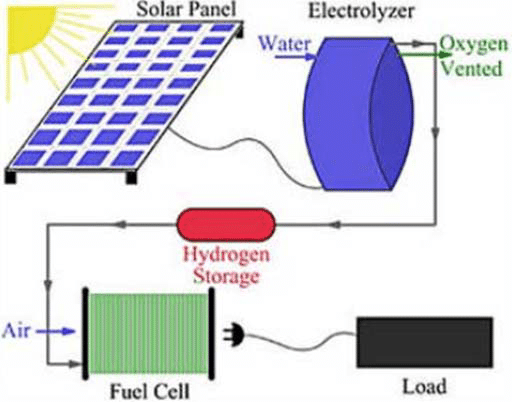
The process of generating hydrogen from solar panels involves a series of sophisticated steps. The primary source of hydrogen is water (H2O). By splitting water molecules, hydrogen can be extracted. However, this process, known as electrolysis, is complex and requires pure water and electrodes. Alternatively, hydrogen can be sourced from the moisture in the air, which is a more cost-effective method.
The Role of Moisture and Air
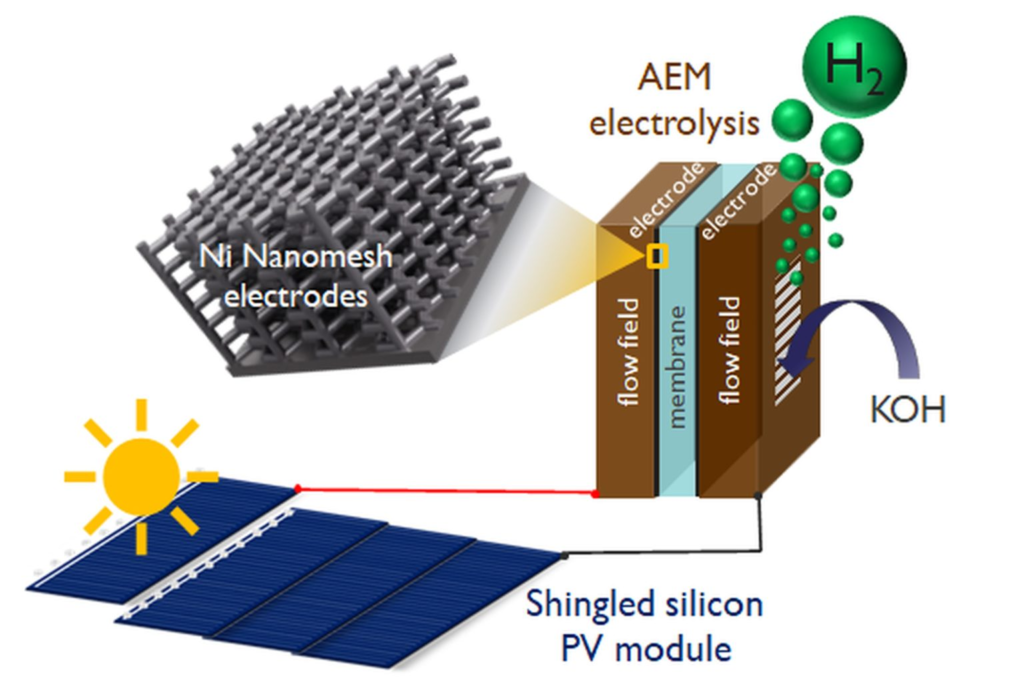
In areas with at least 20% humidity, hydrogen solar panels can efficiently capture moisture from the air. This moisture, when processed, releases hydrogen and oxygen. The panels are equipped with tubes and membranes that facilitate this process. The air passes through these tubes, and the moisture is absorbed by a proton exchange membrane, a sponge-like material that plays a crucial role in separating hydrogen from oxygen.
The Importance of Proton Exchange Membrane
The proton exchange membrane is central to the operation of hydrogen solar panels. It absorbs moisture from the air, converts it into water, and facilitates the separation of hydrogen and oxygen. This membrane is surrounded by layers of anode and cathode, which, with the help of solar energy, generate a small amount of electricity necessary for the separation process.
Generating and Storing Hydrogen
Once separated, hydrogen is stored in tanks for later use. This stored hydrogen can be utilised in various applications, such as powering hydrogen-fuelled vehicles or providing electricity during the nighttime through a fuel cell. The lightweight nature of hydrogen makes it an efficient fuel source, capable of powering vehicles for hundreds of kilometres on a single fill.
The Future of Hydrogen Solar Panels
As technology advances, hydrogen solar panels present a promising alternative to traditional energy storage solutions. Unlike batteries, which require lengthy charging times, hydrogen can be stored and used much like gasoline, offering quicker refuelling for vehicles. This potential makes hydrogen solar panels an attractive option for long-term energy sustainability.

Comparing Hydrogen and Battery Cells
While battery cells are currently more prevalent, hydrogen cells offer several advantages, especially for long-distance travel and industrial applications. As the technology matures, hydrogen solar panels may become a more viable option for everyday energy needs, reducing dependency on fossil fuels and providing a cleaner, more efficient source of power.
In conclusion, the development of hydrogen solar panels represents a significant leap forward in renewable energy technology. As we continue to explore and refine these systems, the potential for a sustainable, hydrogen-powered future becomes increasingly attainable. Whether for home energy use or powering vehicles, hydrogen solar panels hold the promise of a cleaner, more efficient world.
If you’re interested in learning more about solar power and renewable energy technologies, consider exploring online courses that provide in-depth knowledge and practical skills in this exciting field.
